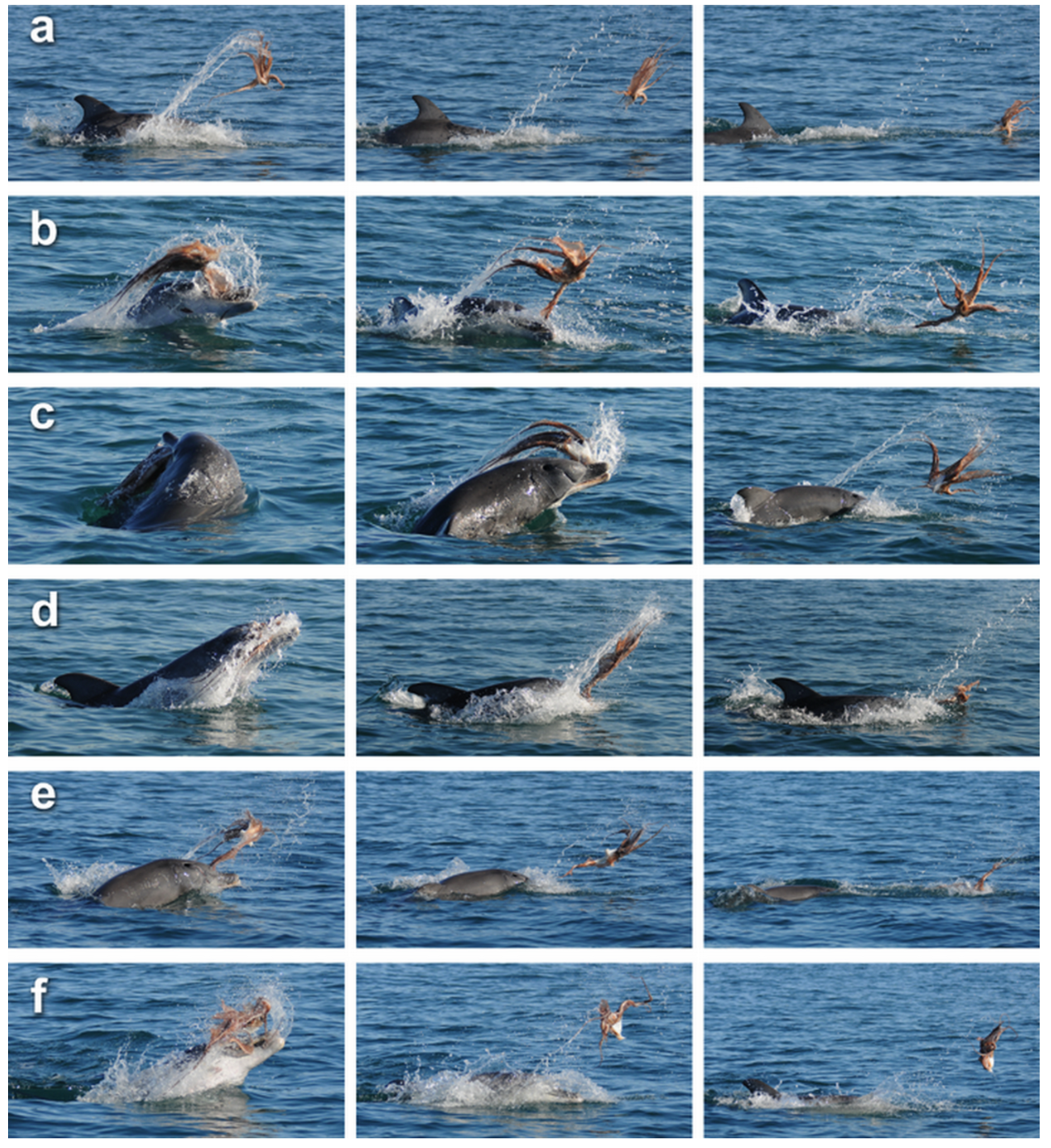
In case you needed further proof that dolphins really are the a$$holes of the ocean, we can now add even more evidence to this list. A new study by Sprogis et al. (2017) includes some pretty badass footage of dolphins “handling” an octopus.
If dolphins weren’t such a$$holes, they would gently cradle the octopus like a kitten, stroking its mantle and respecting the cephalopod’s amazing intellect. But who are we kidding! This is a dolphin we’re talking about, and marine mammal researchers have found that dolphins “shake and toss” cephalopods like a dog tearing apart his favorite chew toy:

Why is this dolphin such an a$$hole to the octopus? Probably because cephalopods are yummy but dangerous food – they’re smart and sucker-y, and dolphins run the risk of *suffocation* if the octopus isn’t fully torn apart and incapacitated before meal time. As Sprogis et al. (2017) found, death by octopus tentacle is surprisingly common:
It is apparent that octopus handling is a risky behavior, as within our study area a known adult male stranded and a necropsy confirmed the cause of death was from suffocation from a large 2.1 kg octopus.1 The dolphin had attempted to swallow the octopus, however, the octopus was found almost intact, with the head and the mantle of the octopus in the dolphin’s stomach and the 1.3 m long arms separated from the head and extending out of its mouth.1 Similarly, another T. aduncus [dolphin] died from suspected asphyxiation due to an octopus lodged in its mouth and pharynx approximately 140 km north of our study area (Shoalwater Bay Islands Marine Park).2 In these two cases, the dolphins may not have processed the octopus sufficiently by shaking and tossing it to ensure the arm’s reflex withdrawal responses were inactive. Octopus arms have a defensive response, as their receptors can detect stimuli that cause damage to their tissues (Hague et al. 2013). These receptors allow octopus arms to continue reacting even after the arms have been detached from the head, allowing the arms to coordinate a reflex withdrawal response (Hague et al. 2013). Dolphins must therefore process the octopus sufficiently to reduce the arms reflex withdrawal response and limit their suckers adhering to them, which otherwise would make them difficult to swallow.
So mad props to all the octopuses out there, for fighting the good fight against dolphins (and sometimes winning!)
Here’s the frame-by-frame photo in all its glory (Figure 1 from the below paper):

Reference:
Sprogis KR, Raudino HC, Hocking D, Bejder L (2017) Complex prey handling of octopus by bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops aduncus), Marine Mammal Science, doi: 10.1111/mms.12405